OVERVIEW
Semaglutide is a long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) developed for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity. It mimics the activity of the natural GLP-1 hormone, which is released after food intake to stimulate insulin secretion, suppress glucagon release, slow gastric emptying, and reduce appetite.
Approved for use under the brand names Ozempic® (for diabetes) and Wegovy® (for weight management), Semaglutide has demonstrated superior efficacy in lowering blood glucose and supporting weight loss, based on over a decade of clinical research.
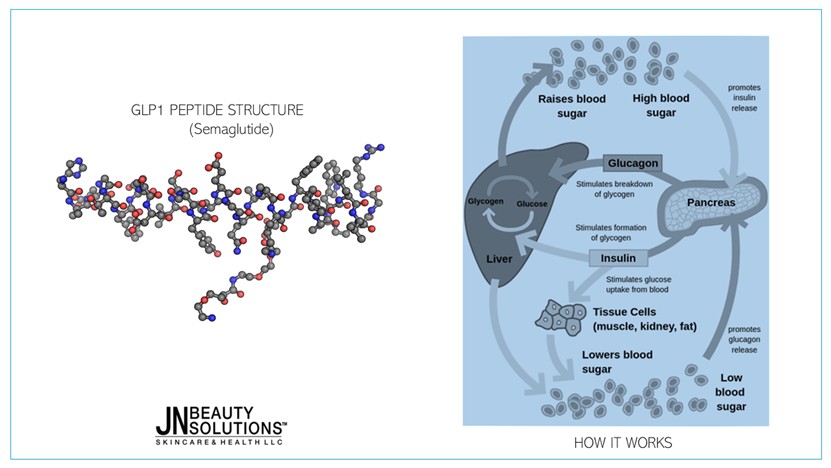
MECHANISM OF ACTION
Semaglutide works by binding to and activating the GLP-1 receptor, leading to:
- Glucose-dependent insulin secretion from pancreatic β-cells
- Inhibition of inappropriate glucagon release from α-cells
- Delayed gastric emptying, increasing satiety and reducing caloric intake
- Central appetite suppression via hypothalamic signaling
- These combined effects result in both improved glycemic control and significant body weight reduction.
PHARMACOLOGICAL MODIFICATIONS
To support once-weekly dosing, Semaglutide was structurally modified for extended half-life (165–184 hours):
- Amino acid substitution at position 8 (Aib) to resist degradation by DPP-4 enzymes
- Acylation at position 26 with a C18 fatty diacid chain for albumin binding and reduced renal clearance
- Additional amino acid substitutions to increase molecular stability
- These changes enable sustained receptor activation with subcutaneous injection once per week.
CLINICAL RESEARCH HIGHLIGHTS
1. Glycemic Control and Dose-Response Relationship
- In multiple randomized, placebo-controlled trials (e.g., Nauck et al., Davies et al.), Semaglutide significantly reduced HbA1c and fasting plasma glucose in patients with type 2 diabetes:
- Dose-dependent reductions in HbA1c observed at doses from 0.2 to 1.6 mg
- Up to 81% of patients reached the ADA HbA1c target (<7%)
- Oral Semaglutide (up to 40 mg daily) also demonstrated strong glycemic effects over 26 weeks
2. Body Weight Reduction
Semaglutide consistently induced statistically significant weight loss across different trials:
- Weight loss up to 4.8 kg over 12–56 weeks at doses of 0.8–1.6 mg
- A high proportion of patients achieved ≥5% body weight loss, with some reaching ≥10%
- Reduction in appetite and caloric intake was not associated with increased nausea or GI distress in most cases
- These effects were observed in both injectable and oral formulations.
ADDITIONAL METABOLIC BENEFITS
Semaglutide also improved a broad range of metabolic markers:
- Lowered postprandial glucose (PPG) and C-max values
- Reduced glucagon levels at higher doses (1.6 mg)
- Improved lipid profiles, waist circumference, and BMI
- Enhanced beta-cell function and insulin sensitivity
- High patient-reported satisfaction via validated diabetes treatment questionnaires
ADMINISTRATION & DOSAGE
- Form: Subcutaneous injection (weekly) or oral tablet (daily)
- Typical Dose:
- Diabetes: 0.5 mg or 1.0 mg once weekly
- Obesity: Escalated up to 2.4 mg once weekly (Wegovy®)
SAFETY AND TOLERABILITY
Common side effects (generally dose-dependent and transient):
- Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, especially during dose escalation
- Mild hypoglycemia, more common when combined with sulfonylureas or insulin
- Rare cases of pancreatitis, gallbladder disease, or renal impairment
- Not recommended during pregnancy, lactation, or in individuals with a history of medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) or MEN2
CONCLUSION
Semaglutide is a clinically validated, next-generation GLP-1 receptor agonist that offers dual benefits: robust glycemic control and clinically meaningful weight loss. With both injectable and oral formulations available, it has become a leading therapeutic option in the global management of metabolic disorders.
For more information, please contact
JN Beauty Solutions™

