WHAT IS COENZYME Q10?
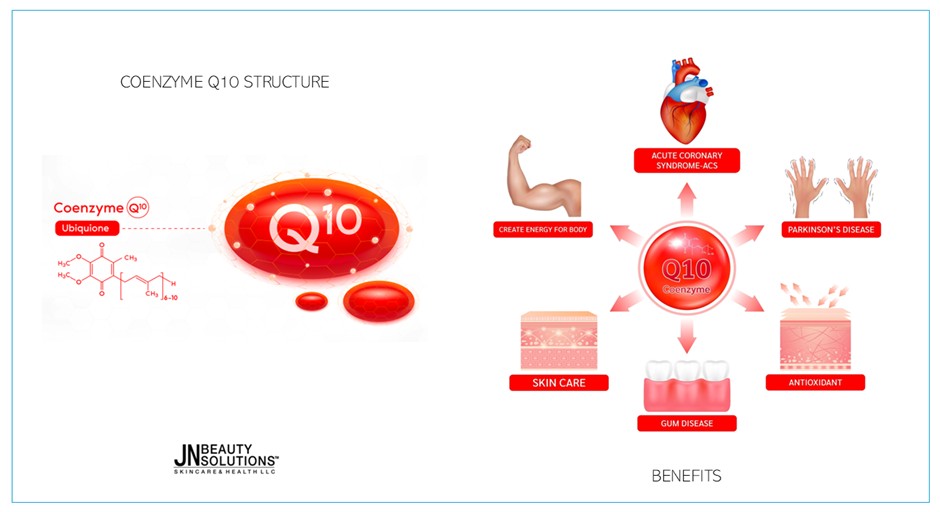
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10), also known as Ubiquinone or Ubiquinol, is a vitamin-like compound naturally present in the body, playing a crucial role in cellular energy production. It is essential in the electron transport chain, a process that generates adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the main energy source for cells.
Coenzymes are organic compounds involved in biological metabolism in the body. Prominent coenzymes often mentioned include Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10), NAD+, and FAD. These compounds act as catalysts, helping enzymes work more effectively during metabolism.
It exists in three different forms: Ubiquinone – the oxidized form of CoQ10, Ubiquinol, the fully reduced form, which has a stronger antioxidant capacity and is more easily absorbed. And the radical semiquinone intermediate form is called Ubl semiquinone.
HISTORY AND RESEARCH
CoQ10 was first discovered in 1957 by scientist Frederick Crane. In the 1970s, more in-depth research began on CoQ10, particularly its role in cellular energy production in mitochondria. CoQ10 has since become a popular supplement, especially in supporting cardiovascular health, energy, and antioxidant protection.
MECHANISM OF ACTION OF COENZYME (COQ10)
CoQ10 plays a vital role in the electron transport chain in mitochondria, the process by which the body generates energy (ATP) from nutrients. CoQ10 helps convert energy from food into chemical energy in the form of ATP. Additionally, CoQ10 acts as an antioxidant, helping protect cells from free radical damage.
CAN IT BE ADMINISTERED INTRAVENOUSLY?
Yes, CoQ10 can be administered intravenously, especially in the form of ubiquinol. This method is typically used when a rapid increase in blood CoQ10 levels is desired, such as in emergencies or for patients with severe cardiovascular issues. However, intravenous administration should be closely supervised by medical professionals.
BENEFITS OF COQ10
- Supports cardiovascular health: CoQ10 helps improve heart function and can support patients with heart failure, hypertension, and coronary issues.
- Antioxidant protection: CoQ10 protects cells from oxidative damage, slows aging, and improves skin health.
- Boosts energy and reduces fatigue: Supplementing CoQ10 may improve energy levels, particularly in individuals with deficiencies due to age or illness.
- Supports neurological health: CoQ10 may benefit neurodegenerative conditions such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease.
- Enhances immune health: By maintaining healthy cells and improving cellular energy, CoQ10 can help the immune system function more effectively.
Using CoQ10, whether orally or intravenously, should be done under medical guidance, especially for individuals with health issues.
BENEFITS OF INTRAVENOUS COENZYME ADMINISTRATION
Intravenous CoQ10 can offer the following notable benefits:
- Enhances energy production: Direct administration into the bloodstream helps improve cellular energy levels and supports cardiovascular health.
- Supports heart function: CoQ10 is commonly used to support cardiovascular treatment, reduce heart failure risk, and improve heart function.
- Potent antioxidant: Intravenous CoQ10 helps the body combat free radical damage more effectively than oral administration.
- Supports brain health: CoQ10 may improve brain function, especially in older individuals or those at risk for neurodegenerative diseases.
RECOMMENDED DOSAGE
The CoQ10 dosage for intravenous administration is typically prescribed by a doctor, with a usual dose of about 100–300 mg. Dosage may vary depending on individual health needs and conditions, with each session lasting about 30–60 minutes.
Cases requiring intravenous CoQ10, such as heart failure or serious cardiovascular issues, should be decided by a doctor, as individual requirements and specific dosages vary by patient condition.
POSSIBLE SIDE EFFECTS OF INTRAVENOUS COQ10
Although CoQ10 is considered quite safe, some side effects may occur, including:
- Allergic reactions: Some individuals may experience allergic reactions to CoQ10 or components of the intravenous solution, causing itching, rash, or swelling.
- Low blood pressure: CoQ10 may lower blood pressure, so caution is advised for people taking antihypertensive medications or with a history of low blood pressure.
- Nausea or vomiting: Some may experience stomach discomfort or nausea after CoQ10 administration.
- Dizziness or headache: This side effect may occur in some individuals due to CoQ10’s effects on blood circulation.
- Liver effects: In rare cases, high doses of CoQ10 over a prolonged period may impact the liver.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Antihypertensive medications: CoQ10 can enhance the effects of antihypertensive drugs, increasing the risk of excessively low blood pressure.
Blood thinners (e.g., warfarin): CoQ10 may reduce the effectiveness of blood thinners, necessitating regular monitoring if use together.
Note: Before intravenous CoQ10 administration, consultation and supervision by a specialist are essential to determine the appropriate dosage and minimize the risk of side effects.
ADDITIONAL RESEARCH
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) has been studied as a supportive agent in cancer prevention and treatment, particularly for improving quality of life and reducing chemotherapy and radiation side effects. However, it is not a mainstream cancer treatment and is generally used as an adjunct therapy. Below are some benefits of CoQ10 in the cancer context:
- PROTECTS CELLS FROM FREE RADICAL-INDUCED DAMAGE
Cancer is a disease related to oxidative damage and gene mutations. CoQ10, with its powerful antioxidant properties, helps protect healthy cells from free radical damage, thereby supporting cancer risk reduction. Free radicals are among the causes of cellular mutations, leading to cancer development. Low CoQ10 levels may impair the body’s defense and increase cancer risk.Some studies indicate that cancer patients often have lower CoQ10 levels than healthy individuals, so CoQ10 supplementation may help maintain the body’s natural defense system.
- IMMUNE SYSTEM SUPPORT
CoQ10 plays a role in enhancing immunity, thereby helping the body combat cancer cells. CoQ10 supplementation has shown potential to improve immune response in some cancer patients. - REDUCES CHEMOTHERAPY AND RADIATION SIDE EFFECTS
Chemotherapy and radiation often damage healthy cells, reduce energy, and cause fatigue. CoQ10 supports cellular energy production and reduces fatigue, helping patients maintain a better quality of life during treatment. Furthermore, some studies suggest CoQ10 may minimize the cardiotoxicity of certain chemotherapy drugs (e.g., doxorubicin). - INHIBITS CANCER CELL GROWTH (UNDER RESEARCH)
Preliminary studies show that CoQ10 may help inhibit the growth of certain cancer cell types. However, these results are limited, and more research is needed to confirm specific effects.
SHOULD COQ10 BE ADMINISTERED INTRAVENOUSLY FOR CANCER PATIENTS?
Intravenous CoQ10 may be used at some medical centers for supportive purposes but should only be administered under specialist supervision.
In some cases, CoQ10 administration may help cancer patients improve recovery and strengthen immunity. However, dosage and frequency must be customized and carefully monitored to avoid unwanted interactions or side effects.
DOSAGE AND USE GUIDELINES
The CoQ10 dosage for cancer support may range from 200–400 mg/day as prescribed by a physician. Higher doses may be administered intravenously in a professional medical setting.
CoQ10 should be used alongside standard treatments such as chemotherapy, radiation, or immunotherapy, and only under professional guidance.
CAUTIONS AND LIMITATIONS
CoQ10 is a supportive method and cannot replace standard treatments. For optimal results, CoQ10 should be sourced from safe, high-quality sources, and medical instructions should be followed. Research on CoQ10 in cancer treatment is ongoing, and further evidence is needed to determine its true effectiveness in cancer therapy.
IMPORTANT NOTE
Although CoQ10 may be a useful adjunct for some cancer patients, it does not replace standard treatments such as surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation. Using CoQ10 in cancer therapy requires the approval and supervision of a treating physician and is generally considered part of a comprehensive supportive therapy.
The information provided above aims to help you better understand Coenzyme Q10 and apply it accurately and appropriately to your needs.
For more product information, please contact:
JN BEAUTY SOLUTIONS™

