GENERAL INFORMATION
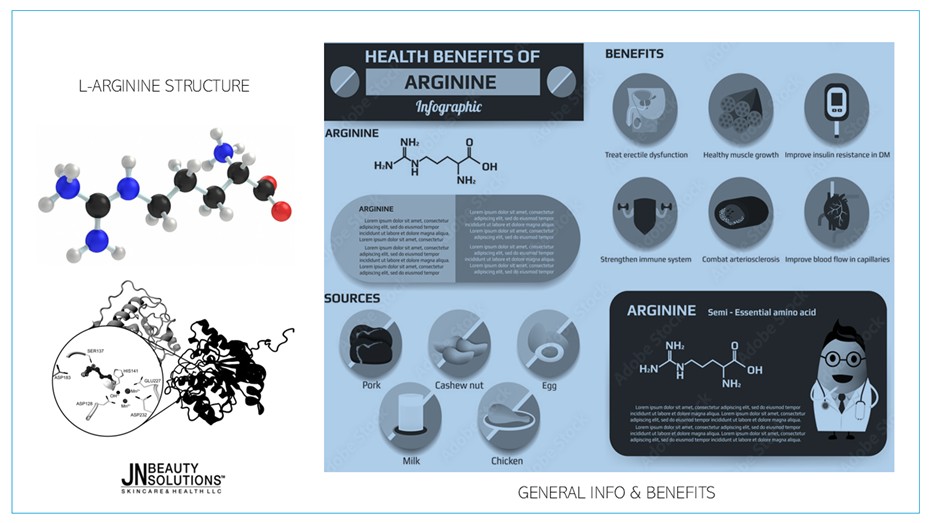
L-Arginine is a semi-essential amino acid that plays a crucial role in many biological processes in the body. It is a precursor to nitric oxide (NO), an important molecule that helps dilate blood vessels, enhance blood circulation, and improve various physiological functions.
L-Arginine is one of the 20 amino acids that make up proteins and is classified as either essential or non-essential. Essential amino acids must be obtained from the diet because the body cannot produce them, whereas non-essential amino acids can be synthesized by the body.
This amino acid is also considered semi-essential or conditionally essential, meaning it becomes necessary under certain conditions, such as pregnancy, infancy, severe illness, and injury.
CHEMICAL FORMULA
Molecular formula: C₆H₁₄N₄O₂
Structural formula: H₂N-C(=NH)-NH-(CH₂)₃-CH(NH₂)-COOH
Molecular weight: 174.2 g/mol
HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT
1886: L-Arginine was first discovered by chemist Ernst Schulze from lupin sprouts.
20th century: Research expanded on L-Arginine’s role in nitric oxide (NO) production, the urea cycle, and cardiovascular health.
1998: Robert F. Furchgott, Louis J. Ignarro, and Ferid Murad won the Nobel Prize in Physiology/Medicine for discovering NO’s role in the body, highlighting the significance of L-Arginine.
MECHANISM OF ACTION
L-Arginine is a semi-essential amino acid involved in several biological processes, including:
- NITRIC OXIDE (NO) SYNTHESIS:
The enzyme Nitric Oxide Synthase (NOS) converts L-Arginine into NO, which helps dilate blood vessels, improve circulation, and regulate blood pressure. - UREA CYCLE:
L-Arginine helps eliminate ammonia through urine by converting it into ornithine and urea in the liver. - PROTEIN SYNTHESIS ENHANCEMENT:
Supports muscle growth, tissue regeneration, and wound healing. - IMMUNE FUNCTION ENHANCEMENT:
Stimulates T-cell production and regulates immune responses. - HORMONE PRODUCTION IMPROVEMENT:
Increase secretion of growth hormone (GH) and insulin, aiding in recovery and growth.
BENEFITS OF L-ARGININE
- IMPROVES BLOOD CIRCULATION AND BLOOD PRESSURE:
Beneficial for individuals with hypertension and cardiovascular diseases. - SUPPORTS ERECTILE DYSFUNCTION TREATMENT:
Enhances erection quality through increased NO production. - BOOSTS ATHLETIC PERFORMANCE:
Improves blood flow to muscles and increases endurance. - PROMOTES WOUND HEALING AND TISSUE REGENERATION:
Stimulates collagen production and new cell growth. - STRENGTHENS IMMUNE FUNCTION:
Supports immune cell production, helping the body fight diseases.
NATURAL SOURCES OF L-ARGININE
Many natural foods contain L-Arginine in small amounts, including nuts (walnuts, hazelnuts, pecans, peanuts, almonds, cashews, Brazil nuts, sesame seeds, and sunflower seeds), oats, corn, cereals, buckwheat, brown rice, dairy products, fish, red meat, poultry, and chocolate. Below are six foods rich in L-Arginine:
- Food Source
- Beef (85g) 1954 mg
- Pork (85g) 1953 mg
- Chicken (85g) 1843 mg
- Pumpkin Seeds (100g) 5353 mg
- Soybeans (110g) 1428 mg
- Peanuts (32g) 804 mg
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Avoid taking L-Arginine without consulting a doctor if you have any of the following conditions:
- Cancer
- Asthma or allergies
- Liver or kidney problems
- Low blood pressure
- Sickle cell disease
- Bleeding disorders
- History of heart attack
DRUG INTERACTIONS
If you are taking any medications or supplements regularly, consult your doctor before using L-Arginine. This amino acid may interact with:
- Birth control pills & hormone therapy
- Blood thinners
- Certain pain relievers
- Erectile dysfunction medications
- Heartburn, hypertension, and diabetes medications
- Supplements containing: Ginkgo biloba, garlic, Asian ginseng, and potassium
L-ARGININE IV ADMINISTRATION GUIDELINES
🔴 Important Note: L-Arginine IV administration must be performed under medical supervision.
Recommended Dosage:
- Therapeutic dose: 5-30 g/day, depending on the patient’s condition.
- Dilution solution: Mix with 0.9% Sodium Chloride (NaCl) or 5% Dextrose to prevent vein irritation.
- Infusion rate: No more than 10 g/hour to avoid sudden hypotension.
- Possible side effects: Flushing, hypotension, nausea, headache, allergic reactions (rare).
- Contraindications: Severe kidney or liver disease, low blood pressure, recurrent herpes (as L-Arginine may stimulate viral growth).
For product inquiries, please contact:
JN BEAUTY SOLUTIONS™

