Introduction to Glutathione
Glutathione is a powerful and essential antioxidant naturally found in plants, animals, fungi, and some bacteria and archaea. It plays a critical role in protecting cells from oxidative stress by neutralizing harmful substances such as free radicals, peroxides, lipid peroxides, and heavy metals.
Chemically, glutathione is a tripeptide composed of three amino acids: glutamate, cysteine, and glycine. It features a unique gamma peptide linkage between the carboxyl group of glutamate and the amine group of cysteine, with glycine attached via a standard peptide bond to cysteine. This structure contributes to its remarkable biological activity and antioxidant capacity.
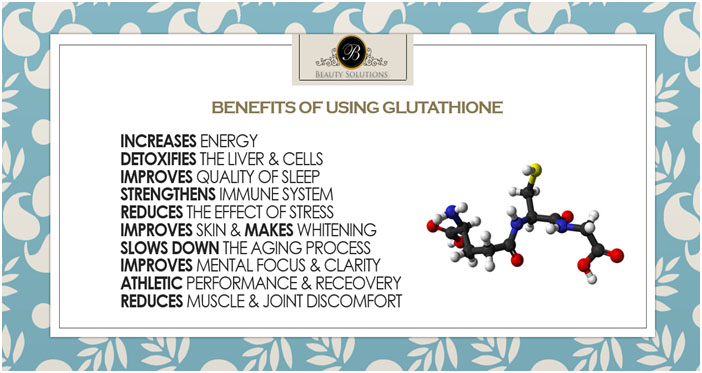
Benefits of Using Glutathione Supplements
1. Skin Health and Appearance
Glutathione is widely recognized for its anti-aging and skin-enhancing properties. It is used both topically in creams and serums, and orally in supplement form.
-
Antioxidant defense: The skin contains high concentrations of antioxidants as a defense against environmental damage. When oxidative stress increases, skin appearance deteriorates.
-
Skin brightening: Glutathione can reduce melanin production—the pigment responsible for skin color—potentially leading to a brighter and more even skin tone. Though its skin-whitening effect is debated, many users and experts report visible improvements.
-
Anti-aging effects: By combating oxidative stress, glutathione helps reduce wrinkles, dryness, and other signs of aging, promoting a radiant and youthful complexion.
2. Immune System Support
Glutathione is fundamental to immune health. Low levels of glutathione (GSH) are associated with weakened immunity.
-
Defense against illness: During illness or infection, glutathione is quickly depleted as the body uses it to fight off pathogens.
-
Preventative function: Maintaining optimal GSH levels enhances the immune system’s ability to respond to and resist illness, making it both a preventive and supportive treatment.
3. Anti-Aging Effects
Oxidative stress is one of the primary contributors to aging. Free radicals damage cells and accelerate signs of aging, both physically and internally.
-
Youthful vitality: By neutralizing free radicals, glutathione reduces cellular damage, increases energy levels, and helps preserve a youthful appearance and feeling.
4. Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Chronic inflammation is linked to numerous diseases including arthritis, asthma, and skin disorders.
-
Reduced inflammation: Low glutathione levels correlate with increased inflammation and oxidative DNA damage. Supplementation may reduce symptoms in conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and chronic pain.
5. Heavy Metal Chelation
Glutathione plays a key role in detoxifying the body by binding to heavy metals and facilitating their removal.
-
Environmental defense: Heavy metals from food, water, and products accumulate in the body, contributing to cognitive decline and cellular dysfunction.
-
Chelation aid: Glutathione helps eliminate toxic metals such as mercury, cadmium, and arsenic, reducing their harmful impact on the body.
6. Master Antioxidant
Often referred to as the “master antioxidant,” glutathione is involved in protecting cells from oxidative stress.
-
Cellular detoxification: It captures and eliminates free radicals and toxins.
-
Recycling capacity: Once oxidized, glutathione can be regenerated in the body, making its antioxidant system highly efficient.
-
Health indicator: A high ratio of reduced to oxidized glutathione is a strong indicator of good health and low cellular toxicity.
7. Liver Health
The liver is the body’s primary detoxification organ, and glutathione is found there in the highest concentration.
-
Liver protection: It reduces inflammation, prevents liver damage, and supports regeneration.
-
Support for detox: People with compromised liver function, whether due to poor diet, alcohol, or environmental toxins, may benefit greatly from boosting glutathione levels.
8. Cognitive Health
Free radicals and heavy metals pose a significant threat to brain health.
-
Brain detoxification: Glutathione is one of the few antioxidants that can cross the blood-brain barrier, allowing it to reduce oxidative damage in the brain.
-
Neurological protection: It may help prevent or slow the progression of cognitive disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease, dementia, and age-related memory loss.
-
Improved function: Regular support of GSH levels may enhance memory, focus, and mental clarity.
Conclusion
Glutathione is a cornerstone of cellular health and plays a vital role in detoxification, immune defense, anti-aging, and overall wellness. Its benefits extend across systems—from glowing skin to cognitive clarity—making it one of the most versatile and valuable antioxidants in the body.
For those considering glutathione supplementation, it’s best to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most suitable form (oral, topical, or intravenous) and dosage based on individual health needs and goals.