WHAT IS MAGNESIUM?
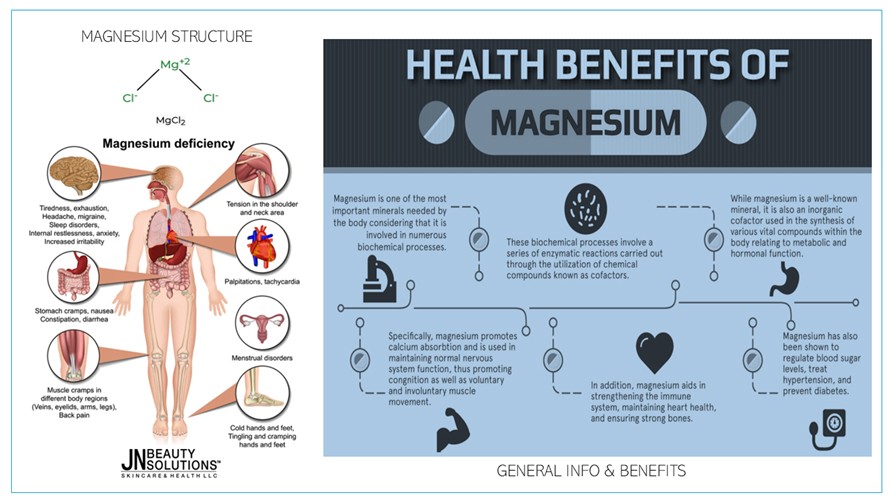
Magnesium (Mg) is an essential trace mineral that plays a critical role in over 300 biochemical reactions in the human body. Naturally found in many foods and available in supplement form, magnesium is vital for protein synthesis, nerve and muscle function, blood pressure regulation, and cellular energy production. About 60% of total body magnesium is stored in the bones, while the remaining 40% is distributed in muscles, soft tissues, blood, and intercellular fluids.
Magnesium also supports Vitamin D metabolism and absorption, making it crucial for bone health. In the gastrointestinal tract, magnesium neutralizes stomach acid and facilitates smooth bowel movement.
CHEMICAL PROFILE
Chemical Symbol: Mg
Atomic Number: 12
Atomic Mass: 24.305 u
Group: Alkaline Earth Metal
Biological Form: Mg²⁺ (ionized form)
COMMON MEDICAL SALTS:
- Magnesium sulfate (MgSO₄)
- Magnesium chloride (MgCl₂)
- Magnesium gluconate
- Magnesium citrate
HISTORICAL BACKGROUND
Magnesium was first identified in 1755 by Scottish chemist Joseph Black. Its name originates from “Magnesia,” an ancient region in Greece where magnesium carbonate (MgCO₃) was found. In 1808, Sir Humphry Davy isolated pure magnesium through electrolysis, marking its official scientific discovery.
MECHANISMS OF ACTION
Magnesium is essential for numerous physiological processes:
- Enzyme Activation: Acts as a cofactor in over 300 enzymatic systems.
- Energy Production: Critical for ATP (adenosine triphosphate) synthesis.
- Electrolyte Balance: Regulates potassium and calcium levels, essential for neuromuscular and cardiac function.
- Nucleic Acid Synthesis: Facilitates DNA and RNA synthesis and repair.
- Neuromuscular Function: Maintains nerve impulse transmission and muscle contraction.
DAILY RECOMMENDED INTAKE (RDA)
Daily Magnesium Intake
- Males 14–18 years 410 mg/day
- Males 19–30 years 400 mg/day
- Males 31+ years 420 mg/day
- Females 14–18 years 360 mg/day
- Females 19–30 years 310 mg/day
- Females 31+ years 320 mg/day
- Pregnant women 350–400 mg/day
- Breastfeeding women 310–360 mg/day
HEALTH BENEFITS
- Cardiovascular Support: Stabilizes heart rhythm, regulates blood pressure, and reduces the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Mental Health & Relaxation: Alleviates anxiety, supports neurotransmitter balance, and reduces stress.
- Bone Health: Works with calcium to preserve bone density and prevent osteoporosis.
- Sleep Regulation: Enhances GABA neurotransmitter activity, promoting deeper sleep.
- Blood Sugar Control: Improves insulin sensitivity, supporting Type 2 diabetes management.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Mitigates chronic inflammation implicated in several diseases.
CAUSES OF MAGNESIUM DEFICIENCY
- Inadequate Diet: Low intake of green vegetables, legumes, seeds, or whole grains.
- Digestive Disorders: Conditions like IBS, Crohn’s disease, or prolonged diarrhea reduce absorption.
- Chronic Illness:
- Diabetes mellitus
- Hyper/hypothyroidism
- Kidney disease
- Substance Abuse: Alcohol, smoking, and excessive caffeine impair magnesium levels.
- Medication Use: Diuretics, proton pump inhibitors, and aminoglycoside antibiotics increase magnesium loss.
- Physiological States: Higher needs during pregnancy, lactation, and aging.
SYMPTOMS OF DEFICIENCY
- Neurological: Fatigue, irritability, depression, poor concentration, insomnia.
- Muscular: Muscle cramps, tremors, spasm, unexplained pain.
- Cardiovascular: Arrhythmias, high or low blood pressure.
- Gastrointestinal: Nausea, vomiting, constipation, bloating.
- Skeletal: Osteoporosis, bone pain, higher fracture risk.
- Metabolic: Insulin resistance, chronic inflammation.
HEALTH RISKS OF DEFICIENCY
- Muscle cramps, seizures
- Sleep disorders, fatigue
- Irregular heartbeat
- Increased risk of hypertension, cardiovascular disease
- Decreased bone mineral density
POTENTIAL SIDE EFFECTS & WARNINGS
Excessive intake of magnesium supplements may cause:
Diarrhea, nausea
Gastrointestinal discomfort
Severe cases: cardiac arrhythmia, hypotension, or renal impairment—especially in individuals with pre-existing kidney conditions.
IV INFUSION MECHANISM OF ACTION
When administered intravenously, magnesium exhibits the following pharmacological effects:
- Cellular Membrane Stabilization
Modulates calcium (Ca²⁺) and potassium (K⁺) transport, stabilizing nerve and cardiac cells. - Vasodilation & Blood Pressure Reduction
Relaxes vascular smooth muscles, commonly used to treat preeclampsia and eclampsia in pregnancy. - CNS Modulation
Acts as a natural NMDA receptor antagonist, reducing excitotoxicity and seizures. - Metabolic Support
Facilitates ATP production and improves insulin sensitivity. - Musculoskeletal Support
Relieves muscle cramps and supports bone mineralization.
COMMON CLINICAL INDICATIONS FOR IV MAGNESIUM
- Severe magnesium deficiency
- Cardiac arrhythmias (e.g., atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia)
- Migraine management
- Preeclampsia/eclampsia in pregnancy
- Acute asthma exacerbations
- Chronic fatigue syndrome
- Hypomagnesemia
TYPICAL IV DOSING GUIDELINES: Condition
- Magnesium Deficiency: 1–4 grams – IV over 1–2 hours
- Arrhythmia/Preeclampsia: 1.5–2 grams – IV over 15–30 min (with maintenance infusion if needed)
- Migraine Crisis: 1 gram – IV over 15 minutes
Dosing should always be tailored based on individual serum magnesium levels and medical supervision.
IV MAGNESIUM SIDE EFFECTS
- Nausea or vomiting
- Hypotension
- Irregular heartbeat (if infused too rapidly)
- Respiratory depression (in overdose)
- Renal strain in patients with impaired kidney function
COMPATIBLE IV COMBINATIONS
To enhance therapeutic outcomes, magnesium is often infused alongside:
1. Energy & Antioxidant Support
Magnesium + Glutathione: Boosts cellular detox and antioxidant defense
Magnesium + Vitamin C: Enhances immune function and skin health
Magnesium + Alpha Lipoic Acid (Thioctic Acid): Supports mitochondrial energy, improves glycemic control
2. Neurological & Sleep Support
Magnesium + B-Complex (B1, B6, B12): Enhances neuroprotection and reduces fatigue
Magnesium + L-Theanine: Promotes calmness and sleep
Magnesium + GABA: Reduces nervous tension and stress
3. Musculoskeletal & Recovery
Magnesium + Calcium (careful ratio required): Supports bones and reduces cramps
Magnesium + Zinc + Biotin: Improves hair, skin, nails, and immunity
Magnesium + GHK-Cu Peptide: Stimulates collagen, skin rejuvenation
4. Cardiovascular & Blood Flow
Magnesium + CoQ10: Enhances cardiac mitochondrial function
Magnesium + Taurine: Stabilizes heart rhythm
Magnesium + L-Arginine: Promotes vasodilation and circulation
⚠️ Caution: Avoid mixing magnesium with phosphate or carbonate in the same IV bag (precipitation risk). Monitor blood pressure when combining with calcium. Use caution with strong diuretics due to excessive magnesium depletion.
CONCLUTION
Magnesium is an indispensable mineral with broad-spectrum health applications, especially when administered intravenously under clinical guidance. At JN Beauty Solutions™, we proudly incorporate medical-grade magnesium into many of our IV health support protocols to promote optimal cellular balance and well-being.
For more information, please contact:
JN Beauty Solutions™

